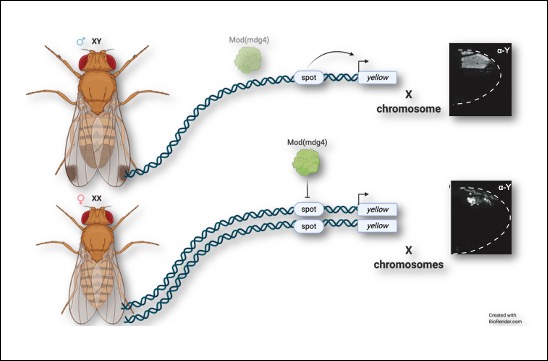
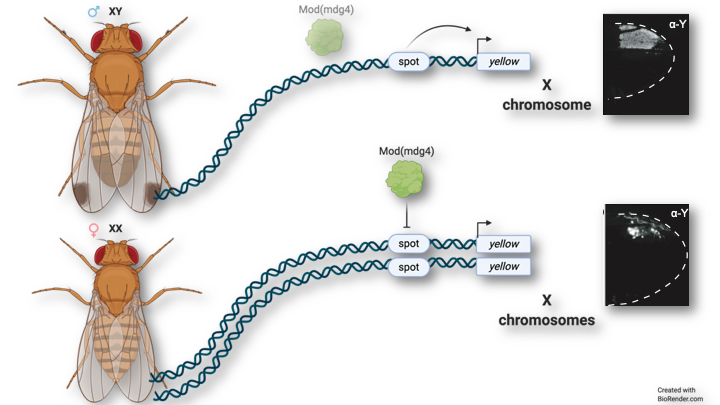
A publication from the Prud’homme team shows how the sexually dimorphic expression pattern of an X-linked gene is controlled by an interallelic interaction, a phenomenon known as transvection. The yellow gene, located on the X chromosome, is involved in the formation of a male-specific wing pigmentation pattern in several Drosophila species. The sexually dimorphic expression pattern of Yellow in the wing is controlled by an enhancer that is active when the gene is present in a single copy, as in XY male, but silenced when the gene is present in two copies, as in XX females. This enhancer is therefore active when it is inherited from one parent, but inactive when inherited from both parents. This work reveals the first example of an interallelic interaction in shaping a morphological difference between the sexes.
To know more :
- Charalampos Chrysovalantis Galouzis, Benjamin Prud’homme. Transvection regulates the sex-biased expression of a fly X-linked gene. Science. 2021 Jan 22;371(6527):396-400.
doi: 10.1126/science.abc2745. PMID: 33479152
Contact
Benjamin Prud’homme – Benjamin.prudhomme@univ-amu.fr