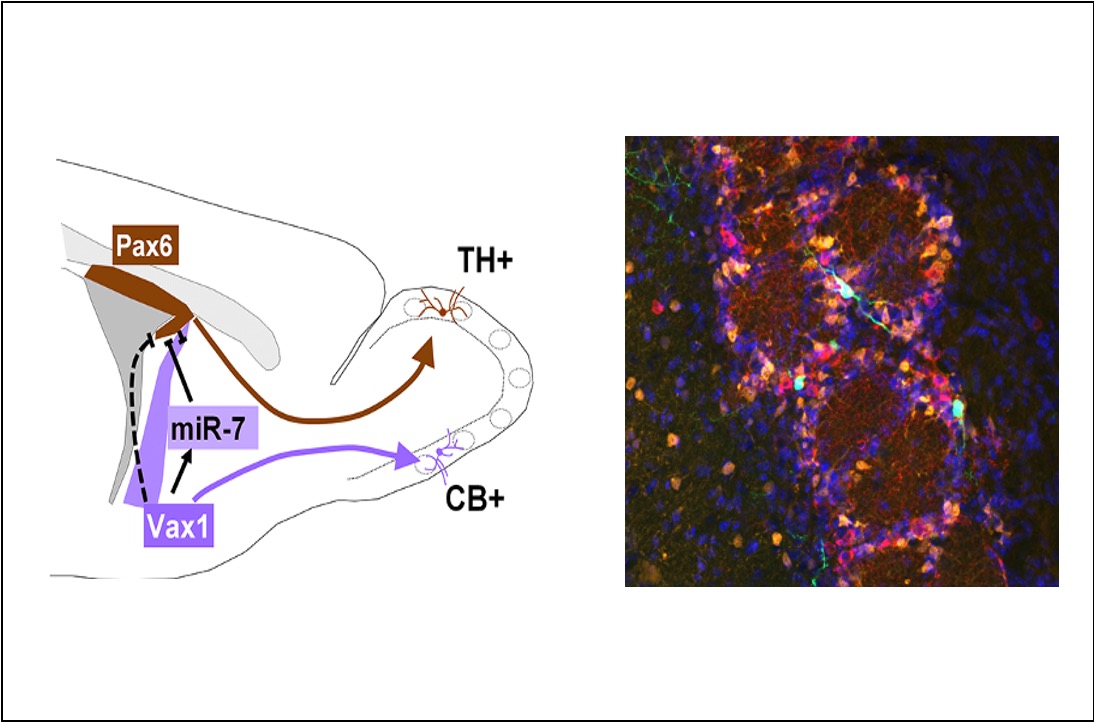
During process of adult neurogenesis, neural stem cells located along the lateral forebrain ventricles generate different subtypes of interneurons for the olfactory bulb. The identity and properties of the neurons that these stem cells produce depend on their relative position in the ventricular wall.
In search for molecular determinants and pathways that control this stem cell regionalization Nathalie Coré found that the transcription factor Vax1 controls the production of two specific neuronal sub-types. First, it is directly necessary to generate Calbindin expressing interneurons (CB+), that are produced from ventral stem cells. Second, it represses the generation of dopaminergic neurons (TH+) by neighboring dorsal stem cells through inhibition of Pax6 expression.
Moreover, with the help of the postdoctoral fellow Andrea Erni, and collaborating with Andy Saurin from the Graba/Saurin team at the IBDM, she found that this repression occurs likely indirectly, via activation of microRNA miR-7.
Funding
This work has been funded by the CNRS, AMU, ANR, FRC and FRM.
To know more :
Coré N, Erni A, Hoffmann HM, Mellon PL, Saurin AJ, Béclin C, Cremer H. (2020)
Elife, doi: 10.7554/eLife.58215