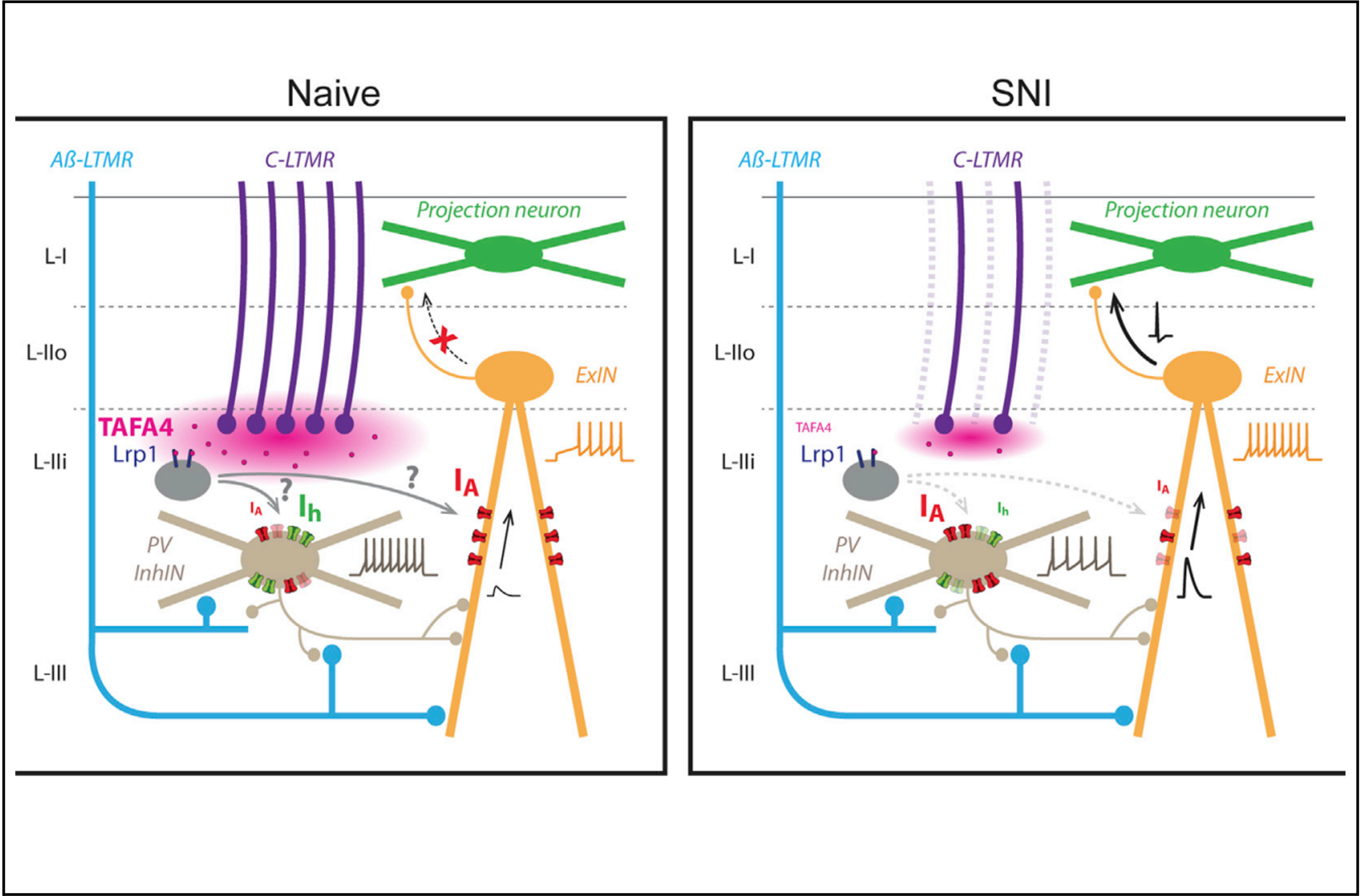
Pain, whether acute or persistent, is a serious medical problem worldwide. However, its management remains unsatisfactory, and new analgesic molecules are therefore required. We show here that TAFA4 reverses inflammatory, postoperative and spared nerve injury (SNI)-induced mechanical hypersensitivity in male and female mice. TAFA4 requires functional LDL-receptors as their inhibition by RAP (receptor-associated protein) dose- dependently abolished its anti-allodynic effect. SNI induces a selective decrease in A-type K+ current (IA) in spinal lamina II outer excitatory interneurons (L-IIo-ExIN), and a concomitant increase in IA and decrease in hyperpolarization activated current (Ih) in lamina II inner inhibitory interneurons (L-IIi-InhIN). Remarkably, SNI-induced ion current alterations in both interneuron subtypes were rescued by TAFA4 in an LDL-receptor-dependent manner. Our findings provide mechanistic insight into the mechanism by which TAFA4 reverses injury-induced mechanical hypersensitivity, by restoring normal spinal neuron activity, and highlight the considerable potential of TAFA4 as a treatment for injury-induced mechanical pain.
To know more :
- TAFA4 relieves injury-induced mechanical hypersensitivity through LDL receptors and modulation of spinal A-type K+ current
Sungjae Yoo, Catarina Santos, Ana Reynders,Irene Marics, Pascale Malapert, Stephane Gaillard, Aude Charron, Sophie Ugolini, Rafaelle Rossignol, Abderazzak El Khallouqi, Jean-Yves Springael, Marc Parmentier, Andrew J. Saurin, Jean-Marc Goaillard, Francis Castets, Nadine Clerc, and Aziz Moqrich
Cell Rep. 2021 Oct 26;37(4):109884. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109884